Navigating the Terrain of Electric Bike Gearing Systems
A very good question we get asked a lot, do electric bikes have gears and do they need to be shifted?
Electric bikes, commonly known as e-bikes, represent a modern fusion of traditional pedaling power with an electric motor. They’ve redefined cycling by offering riders an assisted boost to complete their journeys with less effort and in a more time-efficient manner.
As with their non-assisted counterparts, gears play a crucial role in the performance and versatility of e-bikes, particularly when it comes to managing different terrains and optimizing rider effort.
You Might Like:
Unlocking the Future of Commuting: What are E-Bikes and Why are They Taking Over?
Dive into the heart of electric bike mechanics as we dissect the intricacies of gearing systems. From the hum of derailleur gears to the efficiency of hub gears, we unveil the secrets that keep your e-bike pedaling smoothly. Gear up for a ride through the gears.
Key Takeaways
| Points | Details |
|---|---|
| E-bike Essence | Electric bikes seamlessly blend traditional cycling with an electric motor for assisted rides. |
| Distance Dominance | Ideal for conquering long distances and effortlessly tackling steep inclines. |
| Gearing Galore | Gearing systems optimize rider effort, maintain a comfy cadence, and conserve precious battery life. |
| Gearing Variety | E-bikes boast diverse systems – derailleur gears, hub gears, and continuous gear shifts cater to different preferences. |
| Ratios Rule | Gear ratios influence pedal effort and speed – lower for uphill battles, higher for flat-out speed. |
| Shift Smarts | Proper gear shifting anticipates terrain changes, preventing mechanical strain and ensuring a smooth, efficient ride. |
| System Showdown | Each gear system has pros and cons – from wide-ranging derailleur gears to low-maintenance hub gears and seamless shifts. |
| Gearing Goodness | Understanding and using your e-bike’s gears right adds to joy, boosts battery life, and ensures your bike’s longevity. |
| Maintenance Magic | Regular TLC for your e-bike is a must – it keeps your ride enjoyable, efficient, and ensures the bike’s long life. |
| Diverse Options | E-bikes offer a spectrum of gearing options, catering to varied needs, from daily commutes to weekend escapades. |
| Smart Investment | When investing in an e-bike, consider speed, gear efficiency, and battery life for a savvy, sustainable transportation choice. Visit Is An Electric Bike Worth It? Investing in E-bikes for more insights. |
I. Introduction
Electric bikes have emerged as a popular mode of transportation, combining the physical benefits of cycling with technological enhancements that make riding more accessible to a wider range of people.
By offering varying degrees of powered assistance, e-bikes enable riders to travel farther and tackle steep inclines that might have been challenging without the electric assist. Integral to the functionality of these bikes and their wide range of capabilities are their gearing systems.
What are Electric Bikes?
An electric bike includes all the fundamental elements of a traditional bicycle but is enhanced with an electric motor, which provides additional power to the drivetrain. The motor is usually powered by a rechargeable battery, offering different levels of assist that can be manually adjusted according to the rider’s needs. For detailed insight into how electric bikes function, visit What Are E-bikes?.
The Importance of the Gearing System in Electric Bikes
Just like traditional bikes, gears in electric bikes serve to adjust the bicycle’s torque and speed. They are vitally important for an e-bike’s operation because they enable the rider to maintain a comfortable cadence (pedaling speed) regardless of the travel speed or terrain. Efficient gear use not only ensures a smoother ride but also conserves battery life and reduces strain on the bike’s components.
II. Types of Electric Bike Gears
Electric bikes can come with various types of gearing systems, each with its own method of operation and benefits. Here’s a breakdown of the common types of gears found in electric bicycles:
Derailleur Gears
Derailleur gears are common in both traditional and electric bikes. This system consists of a chain, multiple rear-wheel cogs, and front chainrings, with a mechanism that ‘derails’ the chain to move it from one cog or chainring to another.

Hub Gears
Hub gears, also known as internal gear hubs, are contained within the rear wheel hub of the bike. There are also front mount and dual hub. They function by using internal planetary gears to shift ratios, a system which is generally well-protected from the elements.
Dig Deeper: Classes, Drives & Motors ⬇️
Guide – Selecting The Ideal eBike For Your Needs & Preferences
Continuous Gear Shift: A Seamless Symphony of Motion
Enter the realm of continuous gear shift, a.k.a. continuously variable transmission (CVT). This gear system orchestrates a symphony of smooth transitions, allowing a spectrum of gear ratios without the jolt of traditional gear steps. Picture it as a ballet of efficiency, where your e-bike glides through gears with seamless grace. Smooth transitions while shifting gears, it automatically picks the proper gear.
The CVT Advantage
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Smooth Operator | Experience an uninterrupted flow of power as you pedal, with no discernible gear shifts disrupting your rhythm. |
| Adaptable Riding | The CVT system adjusts effortlessly to your riding style and the terrain, ensuring optimal efficiency. |
| Reduced Mechanical Stress | Without the traditional ‘clicks’ between gears, the CVT minimizes mechanical strain, contributing to a longer lifespan for your e-bike. |
Considerations and Maintenance
| Considerations | Details |
|---|---|
| Complexity | The seamless transition comes at the cost of added complexity, potentially requiring specialized maintenance (internal gearing). |
| Learning Curve | For riders accustomed to traditional gears, adapting to the continuous system might take a few spins around the block. |
In the grand scheme of e-bike gearing, the continuous gear shift is a melody of innovation, offering a ride that’s as smooth as it is efficient. So, gear up for a journey where every pedal stroke is a note in the symphony of motion.
III. How Electric Bike Gears Work
Exploring E-Bike Gear Ratios: Your Key to Enhanced Riding Efficiency
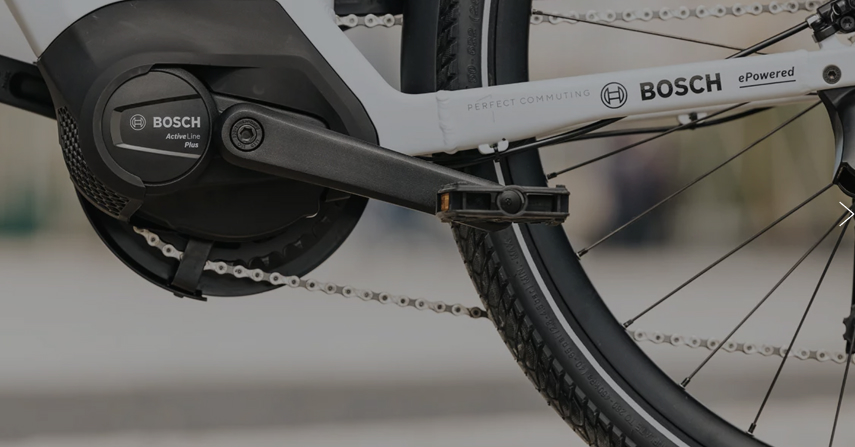

Dive deep into the core of e-bike technology and demystify the critical role gear ratios play in improving your ride. A clear grasp of these mechanical wonders is crucial for achieving peak e-bike performance. Let’s simplify it:
Whats inside the rear hub of mid-drive e-bikes:
- Mid-Drive Motors (Center-Driven):
- Position: Mid-drive motors are nestled in the center of the bike frame, often hidden within the downtube or above the bottom bracket.
- Power Transition: These motors provide a smooth power transition, optimizing efficiency.
- Torque: Mid-drive motors offer plenty of torque, making them ideal for various riding styles.
- Versatility: They can be retrofitted to most bikes, including eMountain, eRoad, eGravel, and eHybrid models.
- Throttle-Assist: Mid-drive e-bikes commonly feature throttle-assist options.
- Chain Interaction: The motor works in sync with the chain, ensuring efficient power delivery.
- Weight Distribution: Mid-drive motors maintain better weight distribution across the bike.
- Aesthetics: Aesthetically pleasing, mid-drive bikes often hide the battery within the frame.
- Hub Motors (Direct-Drive or Geared):
- Position: Hub motors reside in the rear wheel hub (rear-hub motor) or sometimes in the front wheel hub (front-hub motor).
- Torque and Price: Geared hub motors offer more torque and affordability.
- Wheel Spin: These motors “push” the bike forward by spinning the wheel based on sensor inputs.
- Common Use: Rear-hub motors are found on commuter, folding, hunting, entry-level, and throttle e-bikes.
- Challenges:
- Wheel Removal: Rear-hub motors make wheel removal complicated due to their integration.
- Weight Distribution: Weight bias toward the rear wheel affects balance.
- Motor Failures: Excessive torque can lead to motor failures.
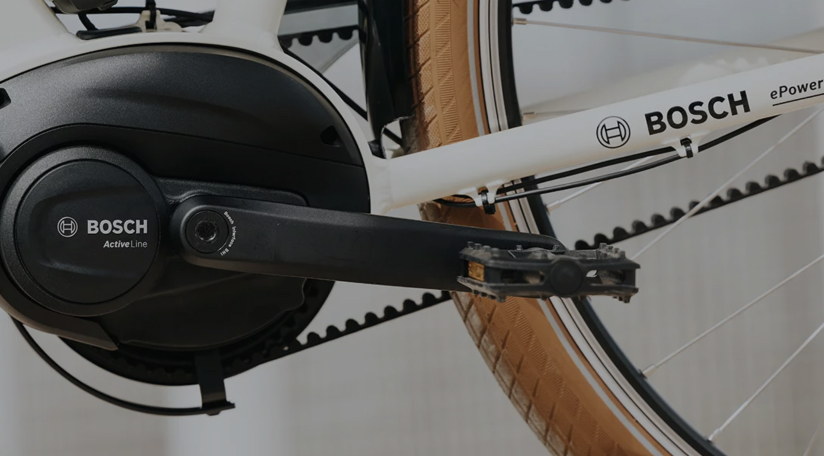


In summary, mid-drive motors excel in efficiency, versatility, and aesthetics, while rear-hub motors offer simplicity and affordability. Choose wisely based on your riding preferences and needs.
Adjust your gear ratios wisely to navigate different landscapes with ease:
| Terrain Type | Ideal Gear Ratio |
|---|---|
| Uphill Climbs | Opt for lower gear ratios to lighten the pedal load on steep ascents. |
| Level Grounds | Higher gear ratios yield quicker paces on even terrain. |
Core Principles of Gear Ratios
The gear ratio acts as the powerhouse, determining the number of pedal turns required to spin the rear wheel once. This ratio is the linchpin that balances pedaling ease and travel velocity.
The Delicate Dance of Gear Ratios
Gear ratios orchestrate your riding experience, from uphill climbs to long, flat stretches:
- Lower Gear Ratios: Tackle steep slopes comfortably, reducing the demand on your legs with more manageable pedal strokes.
- Higher Gear Ratios: Enjoy breezy rides on level paths, where greater ratios translate
Explanation of Gear Ratio
The gear ratio determines how many pedal revolutions it takes to turn the rear wheel once. A lower gear ratio means easier pedaling on uphill terrains, whereas a higher gear ratio is suitable for faster speeds on flat surfaces.
Tailoring Your Ride to the Terrain
Understanding how these gears work, particularly their gear ratios, is essential to optimizing the performance of an e-bike.
Adjusting to Different Terrains
Gears on electric bikes help riders adapt to varying terrains. When climbing a hill, a lower gear will be chosen to reduce the effort needed to pedal, while flat surfaces might see the use of higher gears to reach greater speeds without excessively rapid pedaling.
Different Gears Provide Different Assist Levels

The assist levels on e-bikes work hand in hand with the gears to provide a tailored cycling experience. Depending on the gear engaged, the motor will contribute varying amounts of power to assist the rider, maintaining an optimal balance between pedaling effort and assist.
IV. Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Types of Electric Bike Gears
Each gearing system has its pros and cons. Here’s a brief look:
Derailleur Gears
- Advantages: Wide range of gears; typically lighter and more efficient.
- Disadvantages: Exposed to the elements, requiring regular maintenance; more complex shifting.
Hub Gears
- Advantages: Low maintenance due to protection from debris; simpler to use with less complicated shifting.
- Disadvantages: Often heavier; limited gear range compared to derailleur systems.
Continuous Gear Shift Gearing System
- Advantages: Seamless shifting; no distinct gear steps.
- Disadvantages: Can be more complex technically; potentially higher cost.
V. How to Properly Shift Gears on an Electric Bike
Proper gear shifting is pivotal not only to an enjoyable ride but also to the longevity of an electric bike’s drivetrain components. Electric bikes often require a different approach to gear shifting compared to traditional bikes due to their electric assist feature.
Differences in Shifting Gears
With an electric bike, it’s important to anticipate terrain changes and shift accordingly before the full assist kicks in to prevent mechanical strain. Visit Replacing Ebike Components for advice on maintaining these vital components.
Tips for Smoother Shifting
- Shift gears while pedaling lightly or momentarily reduce pedaling force when shifting, especially on hub gears.
- Use the electric assist setting to your advantage by lowering it when shifting to prevent abrupt gear changes.
- Regularly maintain your e-bike’s gears following the guidelines found in E-Bike Maintenance Guide.
What kind of gear shifting/shifters do most electric bikes have that are mid drive?
| Gearing System | Description |
|---|---|
| Derailleur Gears | Most mid-drive electric bikes utilize a cassette of cogs on the rear wheel and a derailleur guiding the chain up and down, akin to traditional non-electric bikes |
| Twist Shifter | Some mid-drive electric bikes may feature a twist shifter, nestled within the handlebar grip’s inner part, rotated to seamlessly change gears |
| Automatic Gearbox | Rarer systems like the Shimano Di2 boast an ‘automatic gearbox,’ intuitively sensing bike speed and selecting an appropriate gear |
| Hub Gears | Electronically shifting hub gears, exemplified by Rohloff and Enviolo, find their place in some mid-drive electric bikes |
| Thumb-operated Paddles | Mountain and hybrid electric bikes, particularly those with flat bars, often employ thumb-operated paddles for gear shifting |
| Grip Shifters | Some electric bikes opt for ‘grip shifters’ or dials nestled where the rider’s hands rest. Riders rotate the dial forth and back to effortlessly change gears. |
Belt drive vs chain drive for an electric bike (ebike)?
When considering whether to use a belt drive or a chain drive for an electric bike (ebike), there are several factors to take into account. Here are the key points to consider:
Belt Drive vs. Chain Drive: A Comprehensive Comparison
The tables provide a concise comparison of the key factors to consider when choosing between a belt drive and a chain drive for an electric bike (e-bike). It outlines the advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for each drive type, helping riders make an informed decision based on their specific needs and preferences.
Belt Drive
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Low Maintenance | Incredibly low maintenance, cleaner, and smoother, great for commuters |
| Durability | Longer-lasting, can sustain much dirt, suitable for urban commuting |
| Lightweight | Lighter weight than chain drives, contributing to a lighter overall bike weight |
| Quiet Operation | Totally silent, providing a quiet riding experience |
| Disadvantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Limited Gear Options | Selective in gears, operate better with an internal gear hub, limiting e-bike motor choices |
| Cost | More expensive than chain drives, installing a mid-motor for a belt drive can be costly |
Chain Drive
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | More efficient than belt drives at low power outputs, suitable for standard or low-power urban riding |
| Adaptability | Can adapt to either a mid-drive or hub motor, providing more flexibility in motor options |
| Disadvantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Maintenance | May require more frequent maintenance and replacement compared to belt drives |
| Weight | Increases the weight of an e-bike, may fall off, rust, or encounter issues more easily than belts |
| Noise | Can be noisier compared to belt drives |
Considerations
| Factors to Consider | Details |
|---|---|
| Riding Conditions | Consider the type of riding (urban commuting, high-power activities, mountain biking) influencing the choice between belt and chain drives |
| Budget | Chain drives may be a more cost-effective option in the short term; belt drives may offer long-term cost savings due to durability |
| Motor Compatibility | Consider the type of motor for the drive system; belt drives are limited in choice of e-bike motors |
VI. Conclusion
Gears are an integral part of electric bikes, greatly influencing the riding experience, battery efficiency, and overall performance. From the versatile derailleur gears to the robust hub gears or the smooth continuous gear shift systems, e-bikes offer diverse gearing options to cater to the varying needs of riders.
Whether you’re using your electric bike for daily commutes or weekend adventures, understanding and using your gears properly not only contributes to a more enjoyable and efficient ride but also plays a key role in your e-bike’s longevity.
Familiarize yourself with shifting gears on terrains, maintain your e-bike regularly, and always prioritize electric bike safety for the best cycling experience. If you’re considering acquiring an electric bike or wondering if it’s worth the investment, delve into an insightful read on the topic by visiting: Is An Electric Bike Worth It? Investing in E-bikes.
Whether it’s speed, gear efficiency, or battery life that you’re most concerned about, electric bikes offer a world where technology and tradition merge to enable smarter and more sustainable transportation choices. Remember to take care and protect your investment. If you’re in colder frigid temperatures consider winter storage and always perform general maintenance.






